Smithsonian Year of Music
Where science meets music: a banjo player
listens for the songs of katydids
What do playing the banjo and recording katydids have in common? We join Sharon Martinson on Barro Colorado Island to find out.
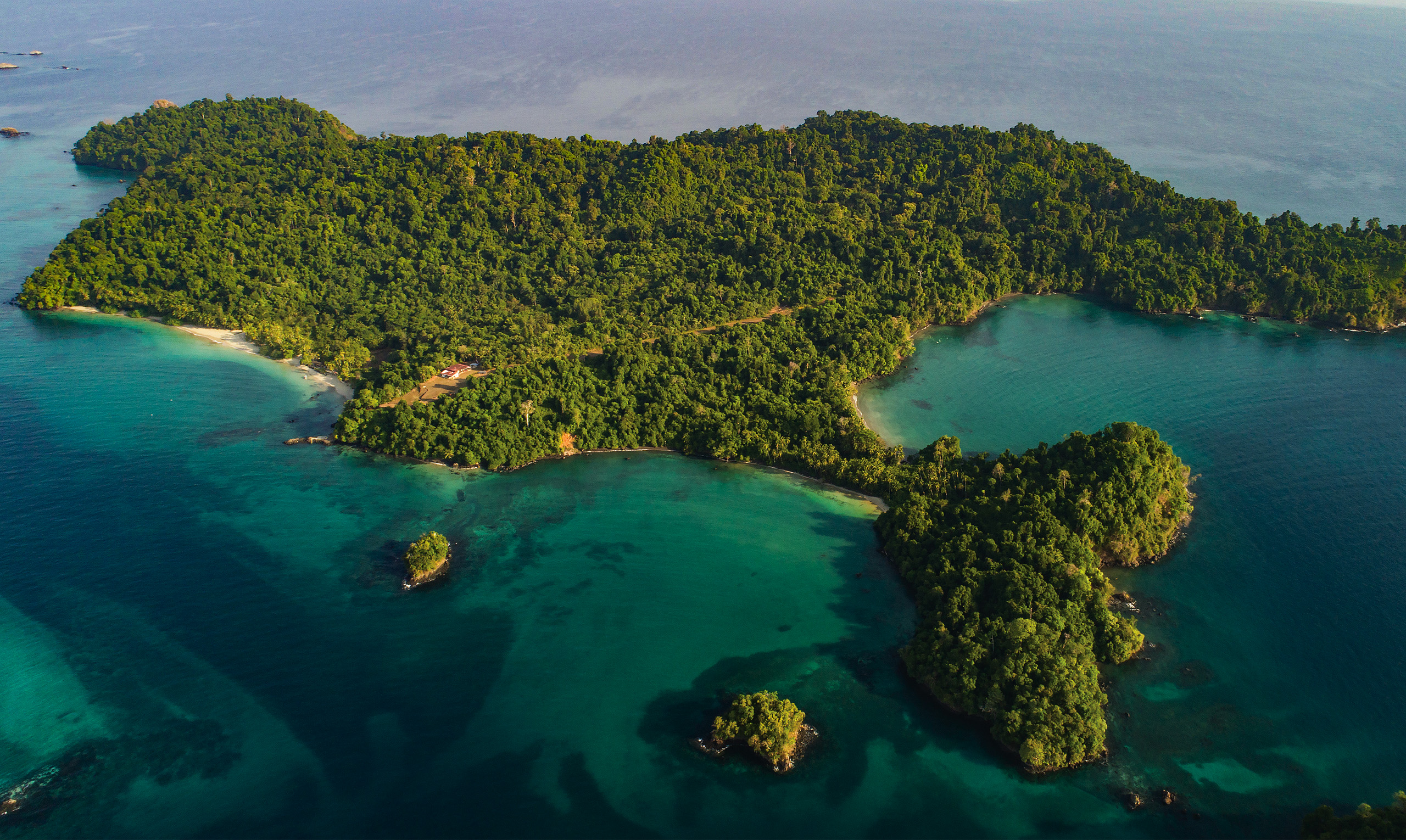
Story location
Barro Colorado
Animal Behavior Evolutionary Biology Biodiversity Ecology Forest Ecology Entomology Connections in nature: Plants, Animals, Microbes and Environments Barro Colorado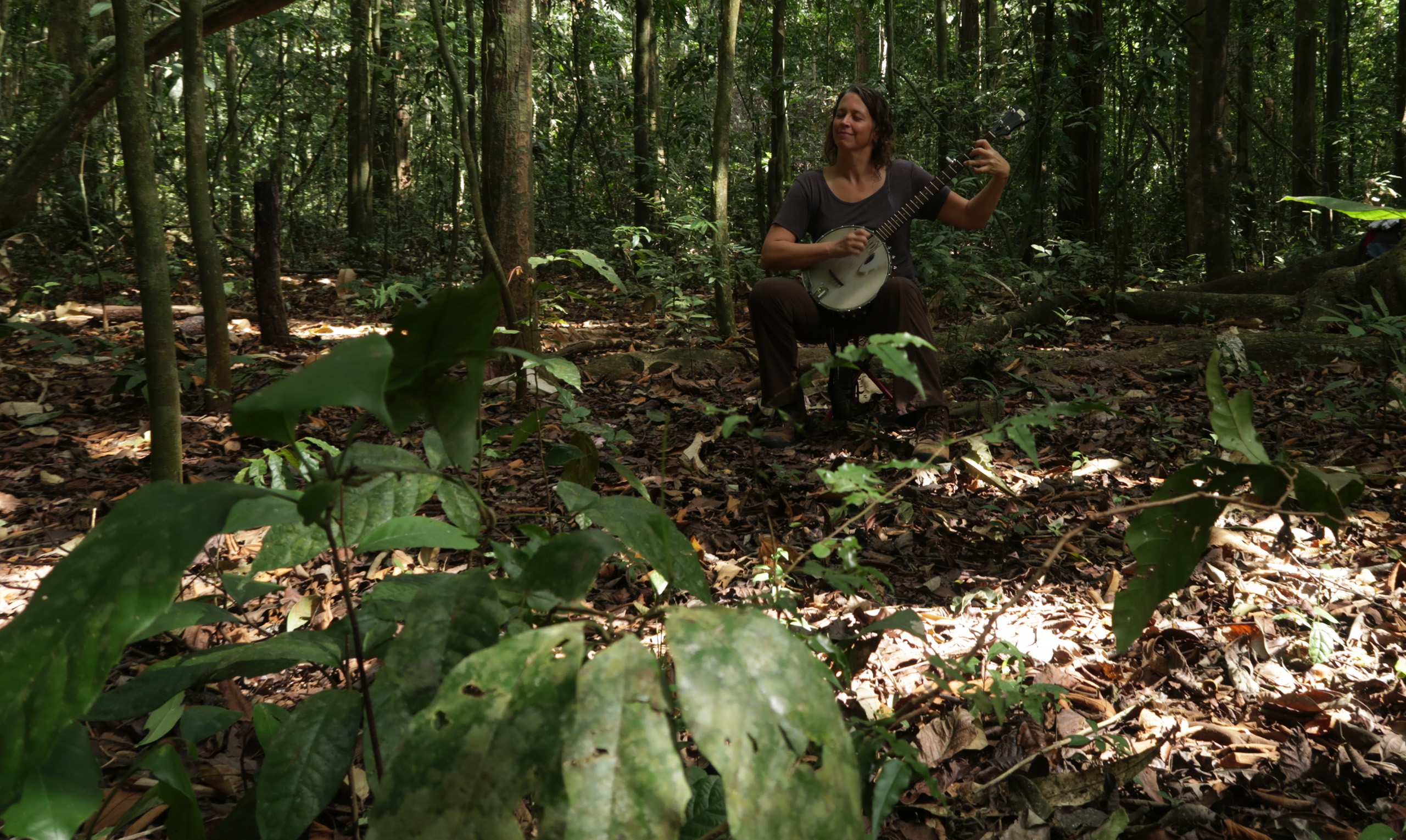 orange
orangeSmithsonian
Year of Music